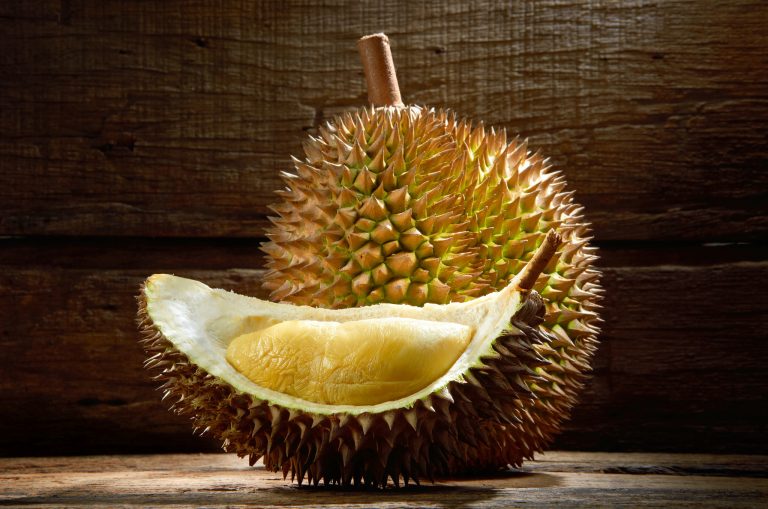
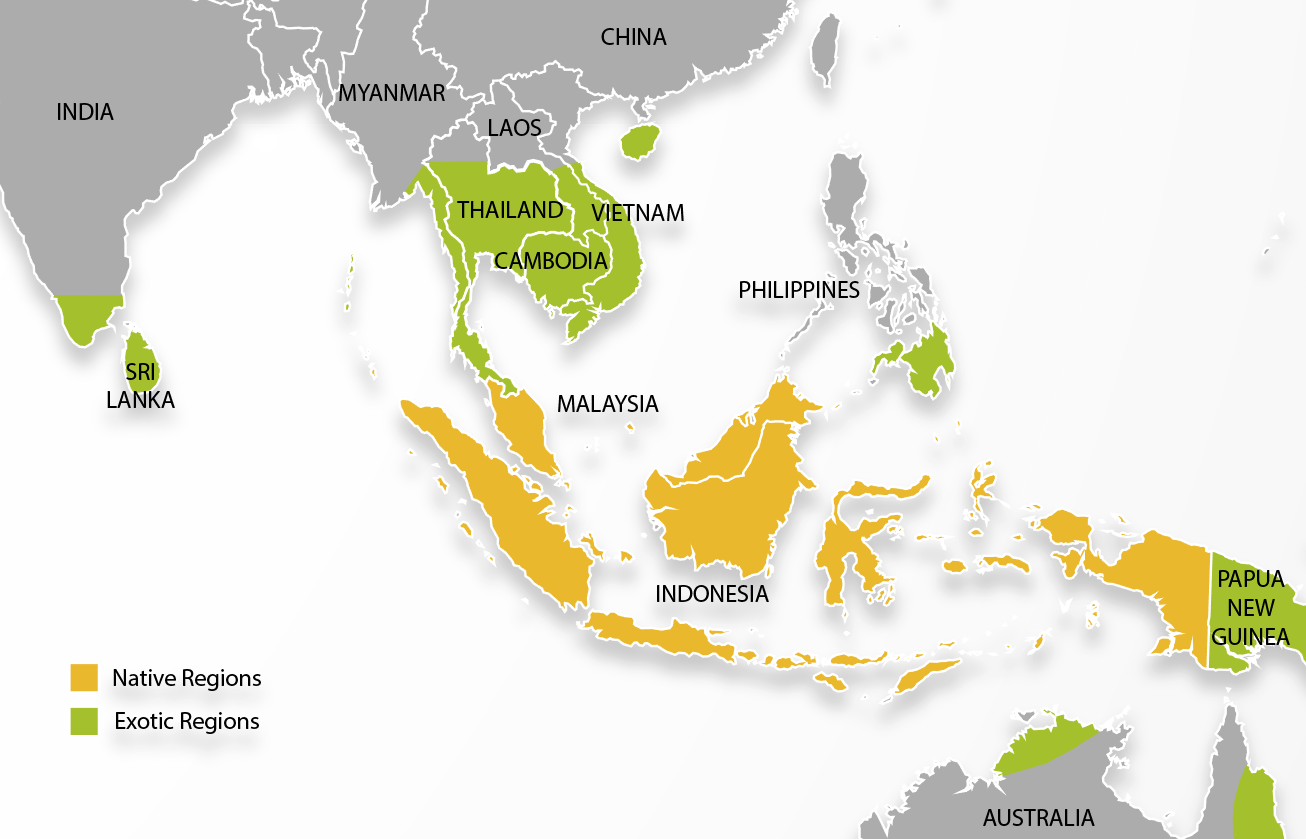
Durian is regarded by many people in Southeast Asia as “The King of Fruits”. The fruit is known for its thorn covering, large size, unique taste and distinctive aroma. The term Durian emerged from the fruits distinctive thorn covering and comes from the Malay word Duri which means thorn. The Durian is believed to have originated from the Malay Archipelago. Although the Durian tree is native to Malaysia, Brunei and Indonesia, it is also grown in Thailand, the Philippines and Australia.

An Asian Delicacy
Durian, once considered a niche fruit is now gaining mass appeal with demand, namely for the Musang King variety, spreading throughout Asia. The Durian tree is a tropical fruit native to Southeast Asia. It grows successfully up to 800m elevation near the Equator and up to 18° from the equator. A well distributed rainfall of 1500 mm and above is needed but dry spells are required as well in order to stimulate flowering and fruit production. It requires a short dry spell of 2 – 8 weeks for flower induction, depending on the Durian variety
Although Durian is native to the Indonesian Malay archipelago it has been grown successfully in other non-native areas to varying degrees that have similar growing conditions. Thailand has been the most successful and is currently the largest producer and exporter of Durian globally followed by Malaysia. Durian is also grown at a smaller scale in the Philippines and other regional countries, mainly for domestic consumption. Additionally Australia has seen some success with Durian known to be grown in northern Queensland on the coastal strip from Tully to Bloomfield River and in the Northern Territory.
Botany and Anatomy
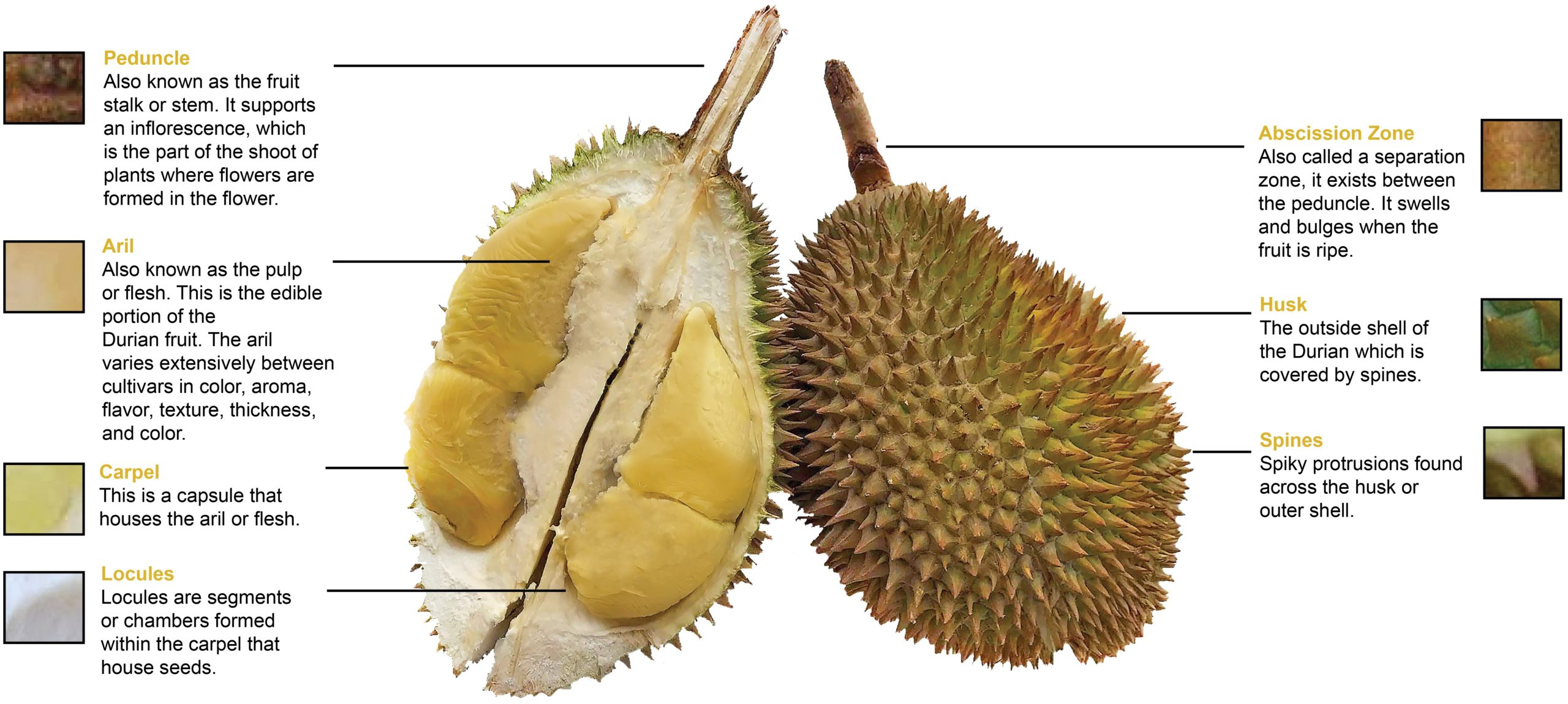
The Durian is the fruit of several tree species belonging to the genus Durio. There are about 30 recognized Durio species and about nine species produced edible fruits of which zibethinus is the most popular and is known as the common durian. Durian fruit is large although weights and shapes can vary. They typically weight between 1 and 5 kg and are pendulous, round to oblong in shape, covered with strong sharp spines or thorns. The husk or pericarp is yellow–green to green or brown in colour and does not change significantly with ripening.
The inside of a Durian fruit is divided into compartments called carpels. Durian may have three to seven carpels although it typically has five. The edible part of the Durian consists of white or cream to golden-yellow colored flesh or arils that are fond inside each compartment. The flesh of Durian fruit varies extensively between varieties in terms of color, aroma, flavor, texture and thickness. As the fruit matures, the flesh softens and the whitish colour changes to cream, yellow or deep orange. The Musang King variety of Durian is the most highly prized of Durian varieties due to its thick and creamy texture combined with a sweet flavor with a hint of bitterness.


Follow us